In this article, we will review some of the most commonly used Linux network management command tools and programs. And explain and explain these commands so that we can better grasp them.
01 ifconfig command
ifconfig is a command line interface tool for network interface configuration. It is also used to initialize the network card interface when the system is started, and can also be used to assign IP addresses to the interface and enable or disable the interface as needed. It is also used to view the IP address, hardware MAC address, and MTU (maximum transmission unit) size of the currently active interface.
Example
ifconfig 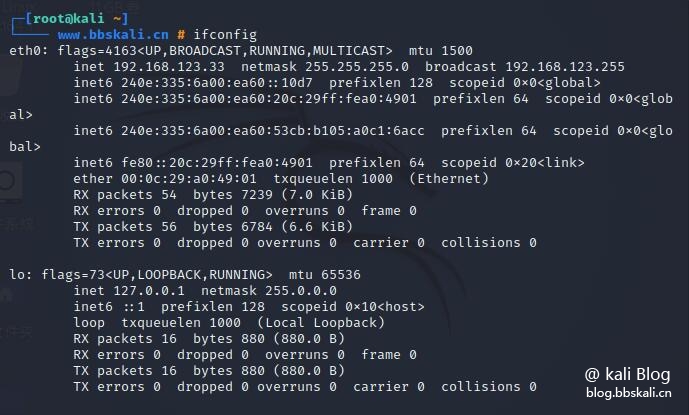
To list all currently available interfaces, whether up or down, add the -a parameter afterwards.
ifconfig -a To assign an IP address to an interface, use the following command.
ifconfig eth0 192.168.56.5 netmask 255.255.255.0 activates the network interface.
ifconfig up wlan0 to deactivate or close the network interface
ifconfig down wlan0 Note: Although ifconfig is a great tool, it is now outdated (not recommended), and its alternative is the ip command explained below.
02 IP command
The ip command is another useful command line utility for displaying and operating routes, network devices, and interfaces. It is a replacement for ifconfig and many other network commands.
Example
ip addr show 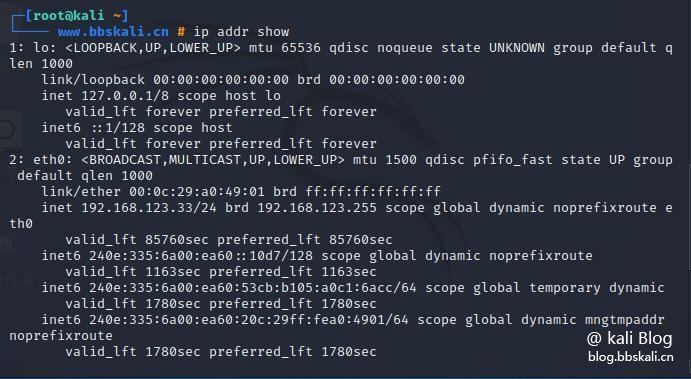
Temporarily assign an IP address to a specific network interface (eth0)
ip addr add 192.168.56.1 dev eth0 To delete the assigned IP address from the network interface (eth0)
ip addr del 192.168.56.15/24 dev eth0 displays the current neighbor table in the kernel
ip neighbor 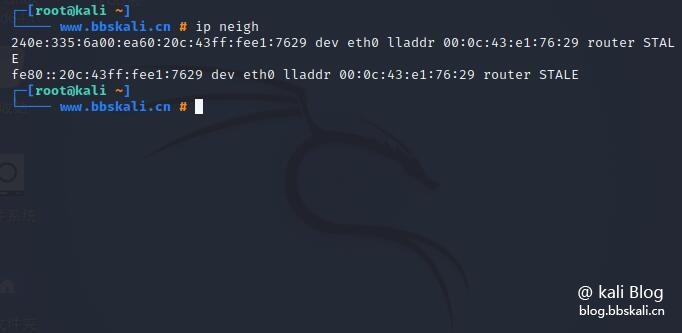
03 ifup, ifdown and ifquery commands
ifup command activates the network interface so that it can be used to transmit and receive data.
The ifup eth0ifdown command disables the network interface, leaving it in a state where data cannot be transmitted or received.
The ifdown eth0ifquery command is used to parse the network interface configuration, allowing you to receive answers to queries about the current configuration method.
ifquery eth0
04 Ethtool command
ethtool is a command line utility for querying and modifying network interface controller parameters and device drivers. The following example shows the usage of ethtool and the command to view network interface parameters.
ethtool eth0 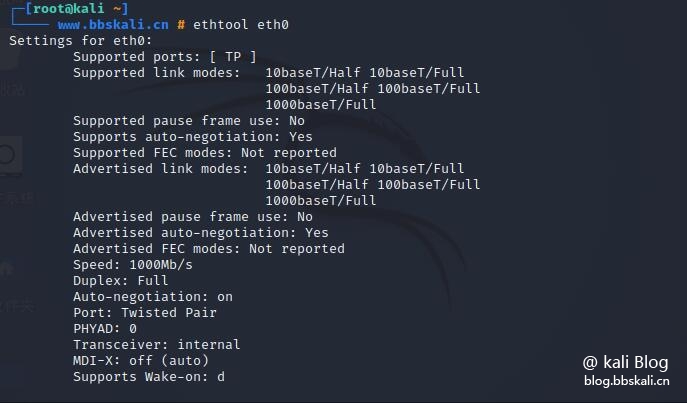
05 Ping command
ping ( Packet INternet Groper ) is a utility that is commonly used to test the connectivity between two systems on a network (LAN) or wide area network (WAN). It uses ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to communicate with nodes on the network.
For example, to test a connection to another node, simply provide its IP or hostname.
ping bbskali.cn You can also use the -c flag shown to tell ping to exit after the specified number of ECHO_REQUEST packets.
ping -c 6 bbskali.cn 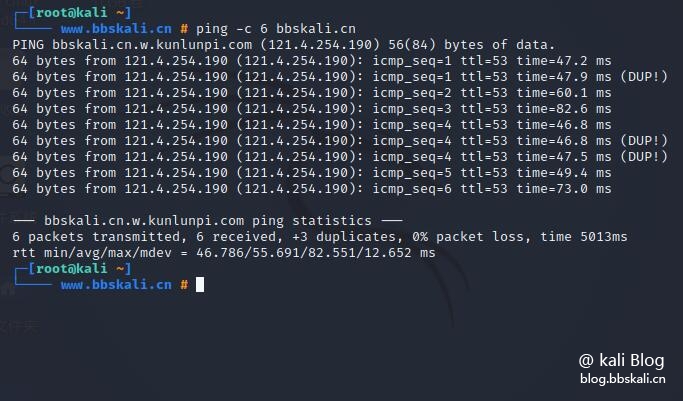
06 Traceroute command
The Traceroute command is used to track the full path from the local system to another network system. It prints many hops (router IP) in the path you reach the final server. It is an easy-to-use network troubleshooting utility after ping commands.
In this example, we are tracking routing packets from the local system to the bbskali.cn server.
traceroute bbskali.cn 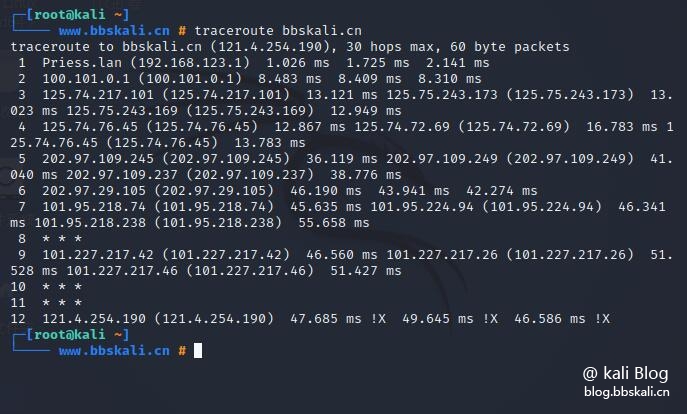
07 MTR
MTR combines the functions of ping and traceroute into a diagnostic tool. By default, its output is updated in real time until you press Q to exit the program.
mtr bbskali.cn 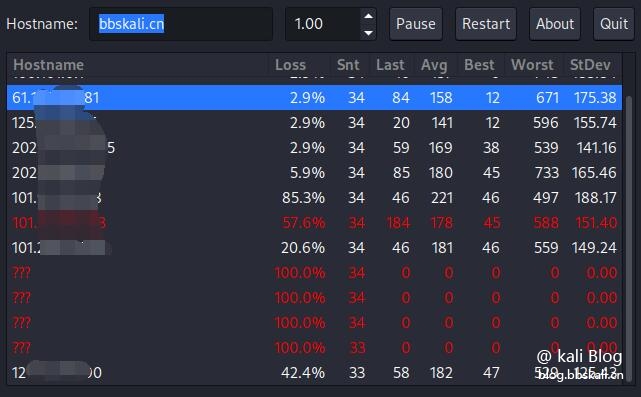
08 route command
route is used to display or manipulate the command line in the IP routing table of the Linux system. Static routing for configuring to a specific host or network through an interface.
route 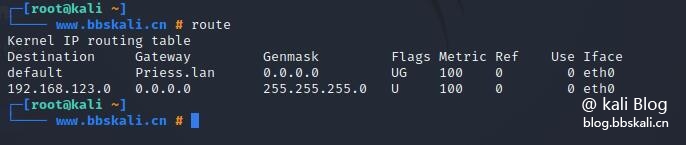
09 Nmcli command
Nmcli is an easy-to-use, scriptable command-line tool for reporting network status, managing network connections, and controlling NetworkManager.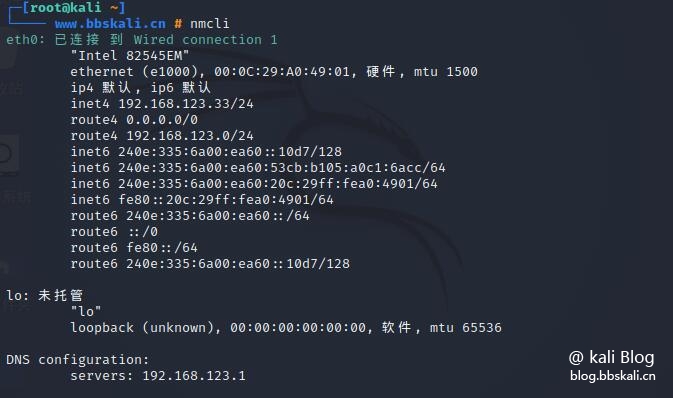
View the current network connection
nmcli con show 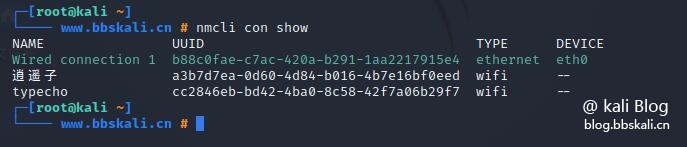
10 Netstat command
netstat is a command line tool that displays useful information about Linux network subsystems, such as network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, and more. It is useful for network troubleshooting and performance analysis.
Additionally, it is a basic network service debugging tool for checking which programs are listening on which ports. For example, the following command will display all TCP ports in listening mode and the program being listened to.
netstat -tnlp view routing table
netstat -r 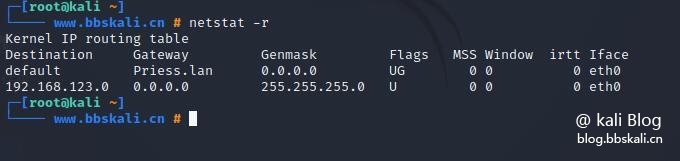
11 ss command
ss (socket statistics) counts TCP information and displays information similar to netstat. Additionally, it shows more TCP and status information than other similar utilities.
Show all TCP ports open on the server 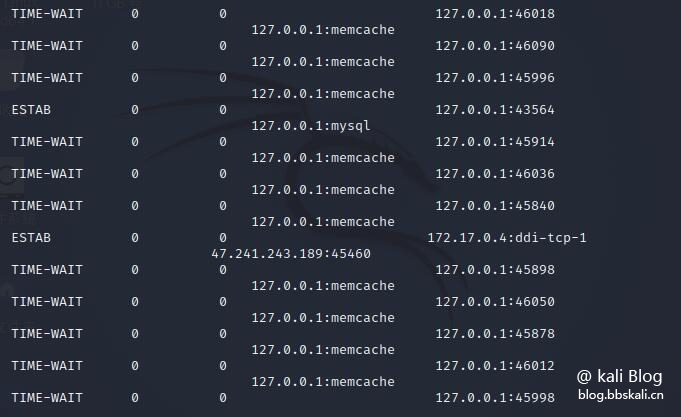
12 nc command
nc is called the "Network Swiss Army Knife" to use it as a simple TCP proxy for network daemon testing, checking whether remote ports are accessible, and so on. Additionally, you can use the nc and pv commands to transfer files between two computers.
Scan the port list
nc -zv bbskali.cn 21 22 80 443 3000 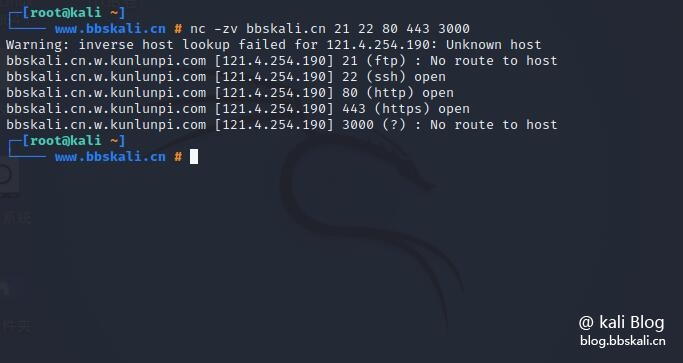
13 Nmap
nmap can be said to be a very familiar tool for everyone, and there were many tutorials before. I won’t talk about it here!
Simple scan
nmap -T4 -A -O bbskali.cn
14 host
A simple utility for performing DNS lookups that convert hostnames to IP addresses and vice versa
host bbskali.cn
15 dig command
Used to query DNS related information, such as A Record, CNAME, MX Record, etc.
dig bbskali.cn 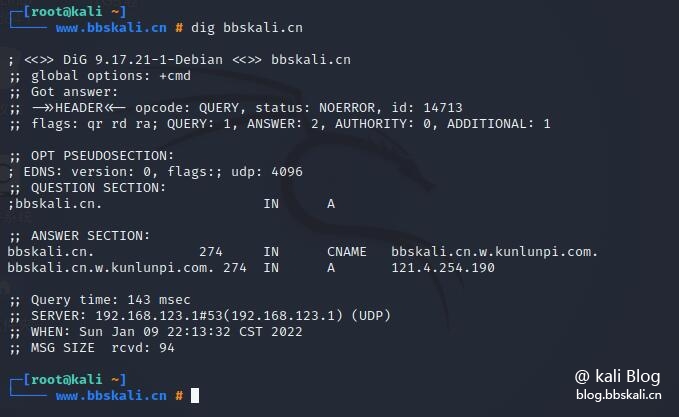
16 NSLookup command
Used to query DNS servers interactively and non-interactively. It is used to query DNS resource records (RR). As shown in the figure, you can find the "A" record (IP address) of the domain.
nslookup bbskali.cn 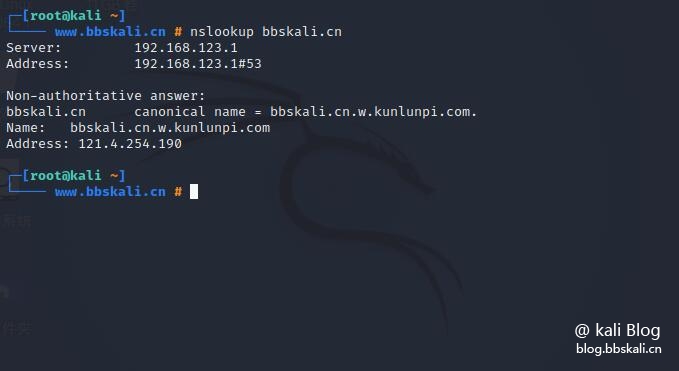
17Tcpdump command
Tcpdump is a very powerful and widely used command line network sniffer. It is used to capture and analyze TCP/IP packets transmitted or received over a network on a specific interface.
For example, to obtain the data packet of the specified network card, you only need to add the -i parameter.
tcpdump -i eth0 You can also capture the packet and save it to a file for later analysis, specifying the output file using the -w flag.
tcpdump -w bbskali.cap -i wlan0 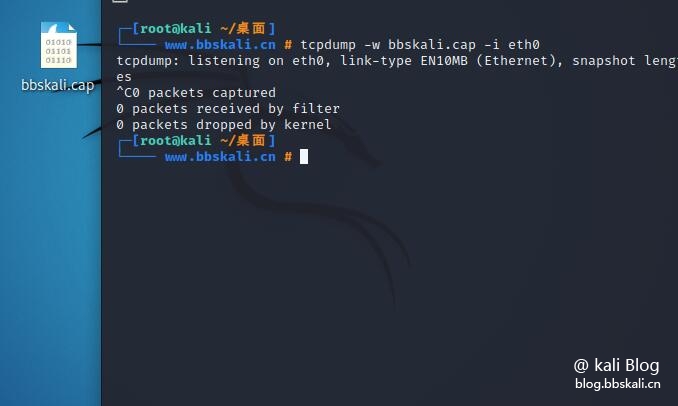
18 Wireshark
Wireshark is a popular, powerful, universal and easy tool for capturing and analyzing packets in a packet-switched network in real time.
You can also save the captured data to a file for later inspection. System administrators and network engineers use it to monitor and inspect packets for security and troubleshooting.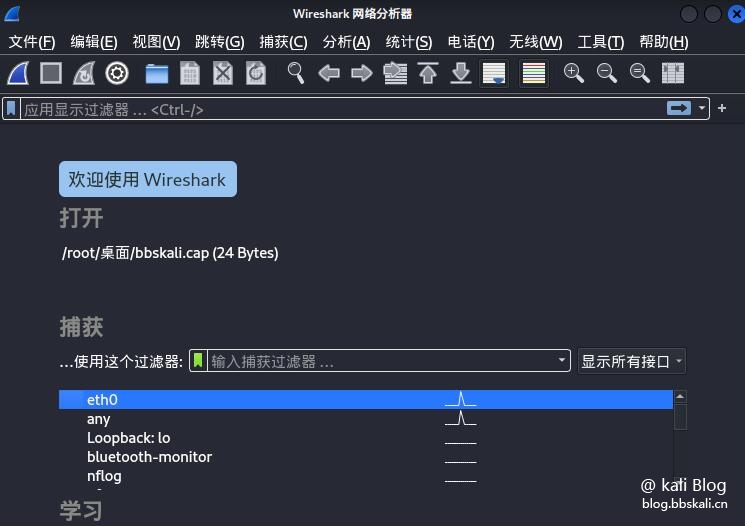
19 Bmon
bmon is a powerful, command line-based network monitoring and debugging utility for Unix-like systems that capture network-related statistics and visually display them in a humanized format.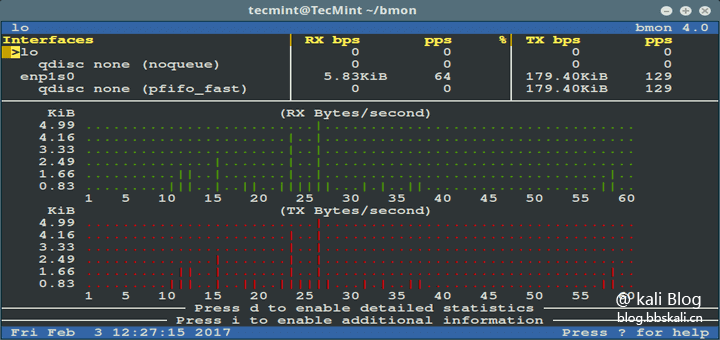
20 iptables firewall
iptables is a command line tool for configuring, maintaining, and checking table IP packet filtering and NAT rule sets. It is used to set up and manage Linux firewalls (Netfilters). It allows you to list existing packet filtering rules; add or delete or modify packet filtering rules; list each rule counter for packet filtering rules.





Recommended Comments